How Does Cloud Management Work in 2022?
Organizations in many sectors use cloud management to optimize data, infrastructure, and services on the cloud. Cloud management techniques also help leverage cloud resources to develop and deploy software applications through APIs. The ultimate goal is to enable growth at scale and provide more flexible data storage, all while reducing cloud costs. Let’s take a look at the main elements of cloud management, and how your organization should approach it.
Elements of Cloud Management
Optimizing data use and app deployments on the cloud requires a combination of special management skills. This includes making important decisions about user responsibilities, team building, software tools, as well as data governance and security. Here are the 5 most important elements of cloud management that any organization should consider when working on the cloud.
Choosing a cloud environment
Businesses need to consider three types of cloud environments: public, private, and hybrid clouds. Most private companies operate in the public cloud, through cloud service providers like Google Cloud, AWS, or Azure. Enterprises can choose to set up their private cloud architecture, with an exclusive data center and on-premises hardware. Banks typically go the private route, to provide extra protection for sensitive financial information.
The hybrid cloud is a mixture of the two. Some companies might prefer a combination of these three options. Naturally, operating in multi-cloud environments will require multi-cloud management. A cloud management platform (CMP) suite solution can help you do this, as they’re designed to simplify the deployment and monitoring of apps across both private and public clouds.
What are your business needs?
A small business will usually require fewer applications and much lower data storage capacity than a large enterprise. They have fewer employees, and certainly fewer IT experts. IT departments will also be smaller, or nonexistent. This means a decreased capacity to manage complex cloud infrastructure on a self-service basis. Having smaller or less specialized purchasing departments can also make it tougher to find the best cloud solutions.
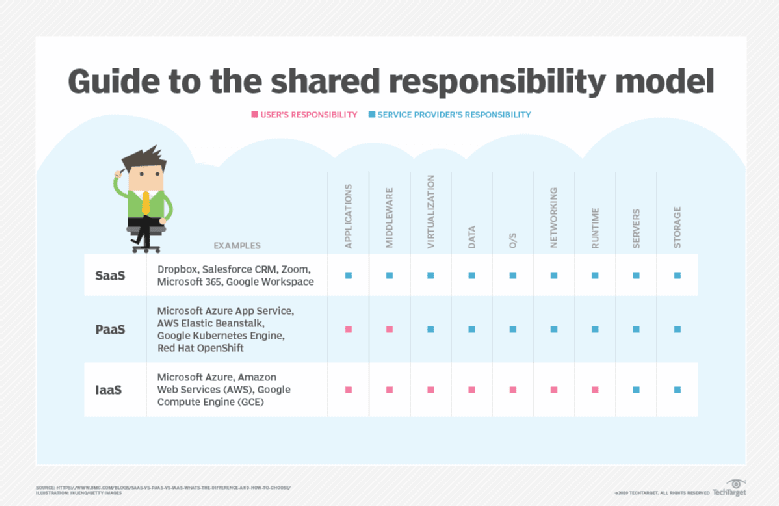
Larger companies would expect to have more control over cloud strategy, cloud platforms, IT infrastructure, and the data lifecycle. To this end, selecting an appropriate cloud computing model – be it SaaS, IaaS, or PaaS, is another decision that data managers will need to take.
Choosing the right computing model can be tough. Small businesses with less technical expertise will tend to prefer SaaS, which provides ready-made software solutions in exchange for a subscription. With SaaS, the software or service provider will do the heavy lifting for you. Due to its focus on app logic, PaaS is ideal for companies that engage in software programming and DevOps.
IaaS provides basic cloud services and is tailored to IT teams trained to engage in configuration management, scaling data usage on-demand. With the provisioning of more flexibility, cost management can be a concern with the typical hourly data use pricing for IaaS.
Keeping policies and best practices up to date
According to a Cybersecurity Ventures report, cybercrime is predicted to cost the world around $6 trillion in 2021 alone. Forecasting for 2025 expects a whopping $10.5 trillion in global costs due to malicious cyber activity. Cloud security is a concern for companies of all sizes, but the risk will tend to increase if there are more users and computing endpoints. Managers will have to decide which cybersecurity consulting services or products are ideal to help protect their data.
Being on the cloud does not necessarily decrease cybersecurity risks, but can reduce the threat of data loss from on-site server damage. To help avoid a data breach, employees should be briefed and trained on basic security precautions to take while in the workplace. This includes how to identify potential phishing and social engineering scams, an ever-increasing threat in the age of social media. Contingency plans for disaster recovery should also be put in place.
In addition to data encryption and protection, cloud managers need to worry about regulatory compliance and data governance, including audits and risk assessments. Service level agreements (SLA’s) and the use of third-party data should be reviewed periodically, as mistakes in data use could lead to fines, lawsuits, or even prosecution.
Picking the right Software
Whether you’re a small startup with limited resources and IT expertise or a Fortune 500 juggernaut, having the right cloud management software can help you execute your management strategy more efficiently.
Cloud management software solutions operate like virtual machines. Performance and data usage costs can be tracked and automated with monitoring tools. Forecasting features with machine learning capabilities can help you determine future data usage and plan resource allocation accordingly.
Open-source tools like the Container as a Service (CaaS) Kubernetes orchestration system can also help with the automation of software deployments on the cloud. Kubernetes can also be used by businesses or individual developers, no matter which computing model or cloud environment they use.
Making the most of human resources
Cloud management introduces the human element to cloud computing. It should establish hierarchies of administrative and user access control for data and applications. Role-based access determines who is responsible for what. Companies look to hire employees who have experience working with public cloud services and/or hybrid cloud environments. This increases the chances of successfully setting KPI metrics and identifying trends.
Skillfully delegating tasks and providing the proper access authorizations promptly can streamline workflows with the optimization of data during every instance of cloud usage, making sure that you stay within your budgets. Management solutions should be put in place to avoid major pitfalls like cloud sprawl, which can quickly cause cloud costs to spiral out of control.
Conclusion: Making the most of the cloud
Skillful management of your various cloud resources can save your business time and money, with more reliable performance. Automation tools can seamlessly track data use, manage cloud instances, as well as project future data needs. Data-backup and governance help make sure that your data stays safe during and after cloud deployments. Though AI and machine learning will continue to improve, there can be no complete substitute for well-managed and informed teams.
For more information on cloud computing, migration management, and software, check out these additional resources on TrustRadius. By comparing reviews from the top Cloud Management Suites in 2022, TrustRadius helps software buyers choose the best provider to improve their user experience while developing software and managing infrastructure on the cloud.
10 Ways Cloud HR Software is Changing the Way HR Works
Cloud Infrastructure and As-a-service Solutions
Cloud Storage Pricing Comparison
7 Benefits of Switching to Cloud-Based Contact Center Software
On Premise to Cloud Migration
Was this helpful?

Looking for your next cloud management software? Start by reading 100% authentic reviews from users just like you.
